Introduction: Pyridostigmine is a medication commonly used for the treatment of myasthenia gravis, a neuromuscular disorder. It belongs to...
Introduction:
Pyridostigmine is a medication commonly used for the treatment of myasthenia gravis, a neuromuscular disorder. It belongs to the class of drugs known as acetylcholinesterase inhibitors, which work by inhibiting the enzyme acetylcholinesterase and thereby increasing the levels of acetylcholine in the body. In this SAR analysis, we will explore the structural features of pyridostigmine and their relationship to its pharmacological activity.
Chemical Structure:
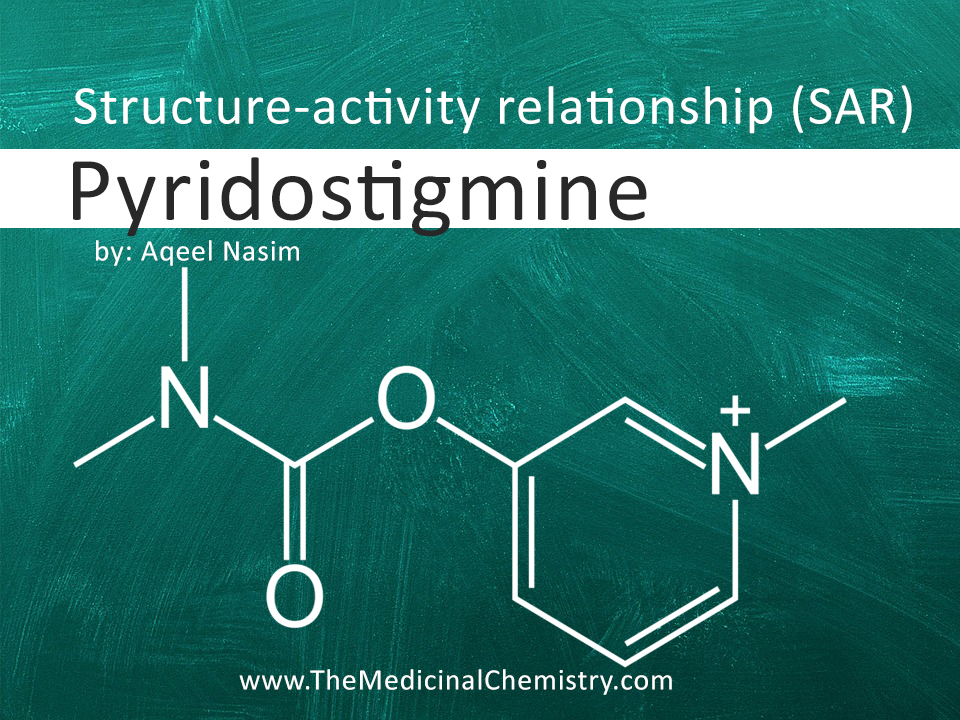
Pyridostigmine has the following chemical structure:
Key Structural Features:
Pyridine Ring: The pyridine ring is a heterocyclic aromatic ring present in the structure of pyridostigmine. It serves as the core structure for the molecule and is essential for its pharmacological activity.
Quaternary Ammonium Group: Pyridostigmine contains a quaternary ammonium group attached to the pyridine ring. This positively charged group is crucial for the interaction of the molecule with the active site of acetylcholinesterase.
Ester Group: Another important structural feature of pyridostigmine is the ester group attached to the pyridine ring. This ester group plays a role in enhancing the molecule's stability and lipophilicity, which can influence its absorption and distribution in the body.
Alkyl Chain: Pyridostigmine possesses an alkyl chain attached to the quaternary ammonium group. The length and nature of this alkyl chain can impact the molecule's potency, selectivity, and duration of action.
Structure-Activity Relationship:
Substitution on the Pyridine Ring: Substituents on the pyridine ring can affect the potency and selectivity of pyridostigmine. For example, the introduction of electron-withdrawing groups at specific positions can increase the molecule's affinity for the active site of acetylcholinesterase.
Quaternary Ammonium Group Modification: Alterations to the quaternary ammonium group can impact the molecule's activity. Changing the size, charge, or substituents on this group can influence the interaction with the active site and modulate the potency and selectivity of pyridostigmine.
Ester Group Variation: Modifications to the ester group can influence the molecule's stability, lipophilicity, and pharmacokinetic properties. Different ester derivatives of pyridostigmine have been synthesized to optimize these properties.
Alkyl Chain Length and Substitution: Changes in the alkyl chain length and substitution pattern can affect the molecule's lipophilicity, potency, and duration of action. Modifying the alkyl chain provides an opportunity to fine-tune the pharmacological profile of pyridostigmine.
Conclusion:
The detailed SAR analysis of pyridostigmine highlights the importance of specific structural features in its pharmacological activity. Modifications to the pyridine ring, quaternary ammonium group, ester group, and alkyl chain can significantly impact the molecule's potency, selectivity, stability, and pharmacokinetic properties. Further exploration and optimization of these structural features can lead to the development of novel derivatives with improved therapeutic outcomes for myasthenia gravis and potentially other related conditions.

No comments